Home | News & Insights | Top 7 Healthcare Tech Trends to Watch in 2024
Home | News & Insights |

22nd Jan, 2024
Digital transformation has become an integral part of many industries, and healthcare is no exception. We have prevsiouly dicussed the benefits of digital transformation in the NHS, with a particular focus on the use of E-Signs electronic signatures and E-Signs e-consent. It is evident that embracing digitalisation has proven to be a game-changer, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving patient care.
Not only are the digital solutions impacting significantly in the healthcare industry but so too are the technological advances. From the creation of the smallpox vaccine in 1977, to artificial intelligence (AI) assisting medical professionals in diagnosing and treating illness, technological advancements in healthcare enable humans to live longer, healthier and happier lives across the world.
As new technologies emerge in the healthcare industry, we begin to enter unchartered waters. Technology such as AI and virtual health look likely to dramatically change everything from how we develop medicine and patients to the business and commercial side of the industry.
With these factors in mind, we have listed what we believe are the most prominent and disruptive technology trends in healthcare for 2024.
The healthcare sector is experiencing a transformative shift driven by the AI revolution. While scepticism exists, a rising number of people are optimistic about its current applications. The global AI in the healthcare market was valued at 16.3 billion US dollars in 2022 and is expected to grow to reach 173.55 billion US dollars in 2029. Looking into 2024, generative AI is expected to elevate the efficiency of healthcare professionals, enabling them to perform their duties with enhanced speed and precision.
Presently, this technology is capable of condensing extensive medical research and clinical notes, significantly expediting the development of healthcare solutions. By tackling routine tasks that traditionally consume a considerable portion of healthcare professionals’ time, AI emerges as a key player in addressing chronic staffing challenges faced by hospitals. Furthermore, its role in disease diagnosis, particularly through advanced imaging, is expected to expand, contributing to a more comprehensive healthcare landscape.

Throughout 2023, AI has undeniably taken centre stage; however, augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) technologies have been steadily but speedily gaining traction in the healthcare industry. Meta’s recent launch of Oculus III, a more affordable and accessible AR/VR headset, and Apple’s introduction of Apple Vision Pro, a high-threshold counterpart, signifies a growing presence and accessibility in the industry.
Both Meta and Apple are actively promoting applications in healthcare, leveraging their extensive user bases and established infrastructures. These advancements hold the potential to bring about a profound transformation in medical training, extending to clinical and surgical care. While AR/VR technology is still in its early stages, facing privacy and safety concerns similar to the adoption of AI, it could emerge as the dark horse of 2024, surpassing the fleeting excitement surrounding technologies like generative AI.
Simply put, personalised medicine refers to the creation of tailored treatment plans for individual patients. Although ways of doing this have been done before, medical professionals are becoming more reliant on genomics to assist them. Genomics uses AI to analyse patients DNA to accurately diagnose and treat diseases and create medicines that are personalised to the individuals down to the molecular level.
Numerous experts argue that adopting an individualised approach to healthcare results in more positive patient outcomes and the more optimal utilisation of medical resources. This approach is expected to assume a progressively vital role in tackling the forthcoming challenges in the healthcare landscape.

Hands free communication and monitoring is one of the emerging technology trends in healthcare that is continuing to expand. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the industry had to adapt and look at other ways to help patients, this played an important role in the care of patients who could not physically attend medical appointments.
E-Sign played a critical role in the digitisation of prescriptions in the UK working alongside the National Clinical Homecare Association (NCHA). The goal was to a universal and scalable solution that addresses all of the issues relating to paper-based prescription transport. The key results of the project were;
Advanced technology, termed “Remote Patient Monitoring” (RPM), empowers healthcare practitioners to monitor a patient’s well-being from a distance. This innovation proves especially beneficial for elderly individuals or those with chronic illnesses who necessitate consistent monitoring and attention but face challenges attending in-person appointments.
RPM leverages the Internet of Medical Things alongside specialized digital health devices like glucose meters and blood pressure monitors. Applications linked to these devices efficiently gather data and promptly notify healthcare providers in the event of irregularities. Consequently, RPM systems are anticipated to evolve into a pivotal element in delivering continuous care for individuals facing heightened health risks.
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) in the healthcare sector is progressing, marked by the increasingly popular concept of virtual hospitals and the evolution of Telemedicine 2.0. This transformative trend harnesses technology to overcome geographical barriers, facilitating patients in receiving medical care within the confines of their homes, while maintaining seamless connectivity with healthcare providers.
This trend includes both telemedicine and wearable devise, connected to the global network. By using connected devices to remotely monitor patients and provide communication channels for healthcare professionals, more aspects of care can be delivered remotely. With Saudi Arabia bringing to life the first virtual hospital in 2023, it’s clear that the concept of virtual hospitals and wards are quickly becoming a reality.
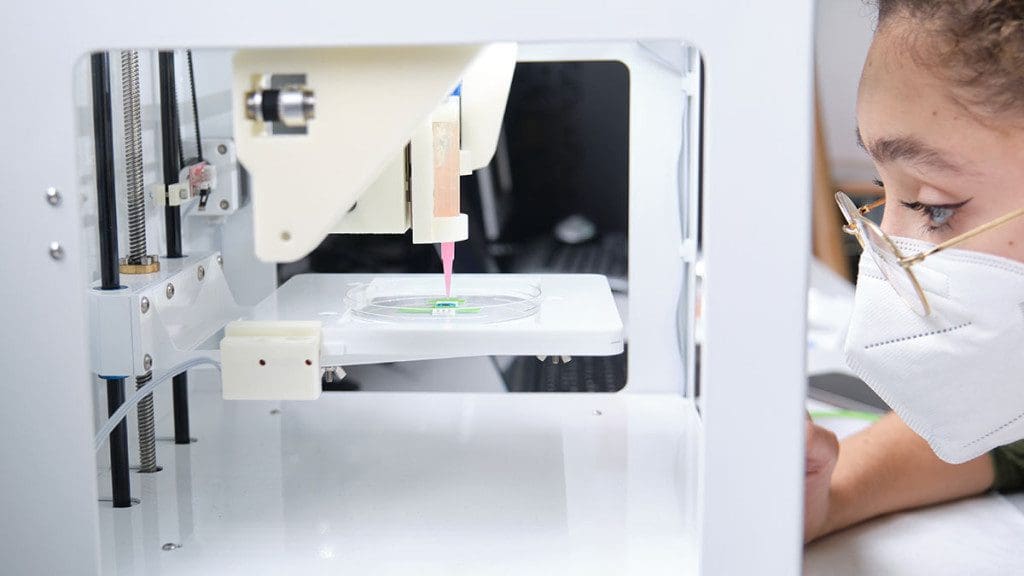
While 3D bioprinting has been present in healthcare for some time, its capacity to replicate three-dimensional structures akin to natural tissues is capturing the interest of scientists and researchers. The latest advancements in prosthetic treatment, coupled with the integration of AI and other refined technologies, suggest an imminent surge in the adoption of 3D bioprinting. This development holds the promise of mitigating the high costs associated with implants and prosthetic treatments.
Furthermore, patients are witnessing an expanding variety of options, particularly in the realm of cardiovascular and neurological implants, thanks to the capabilities of 3D bioprinting. The technology is poised to make significant contributions to the enhancement of bionic knee and hip prostheses, offering improved solutions for individuals in need of such procedures. As these innovations continue to evolve, 3D bioprinting is likely to play a pivotal role in reshaping the landscape of prosthetic treatments and implant procedures.
The value of data has reached unprecedented heights, even as its exponential growth persists. The healthcare industry was traditionally slow to embrace data digitisation however has now found its data volume surpassing that of manufacturing, financial services and media industries. According to a Market Research Future report, the healthcare data storage market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 15.3%, reaching an estimated $69.31 billion by 2032.
Blockchain technology, emerging as one of the predominant trends in healthcare IT, offers a solution for efficient digital information storage that occupies significantly less space. In the ongoing battle against ransomware, healthcare professionals are prioritising robust infrastructure to better mitigate risks. Recognising blockchain’s potential in enhancing cybersecurity and addressing data safety concerns, this storage method emerges as an ideal approach to preserving information authenticity.
E-Sign Helps to Digitally Transform Healthcare Organisations

E-Sign offers complete eSignature and digital document solutions for healthcare organisations. By eliminating paper-based administration, the healthcare sector not only stands to benefit from substantial time savings but also cost savings. Think about all the areas of healthcare that still rely on paper-based processes, such as:
With E-Sign’s digital signature and document management platform, you can eliminate paper-based administration, moving these processes online to improve efficiency, reduce turnaround times and improve productive collaboration between your employees. Digitalisation goes a long way to improve overall user experience, making it easier for your students and staff to complete, sign and return forms, with no inconvenience or cost to them.